
/GettyImages-1146508242-ec8ea59253274282bcb2324b15e87b90.jpg)
Household incomes fall and the economy slows down during a recession, and government tax revenues fall as well.
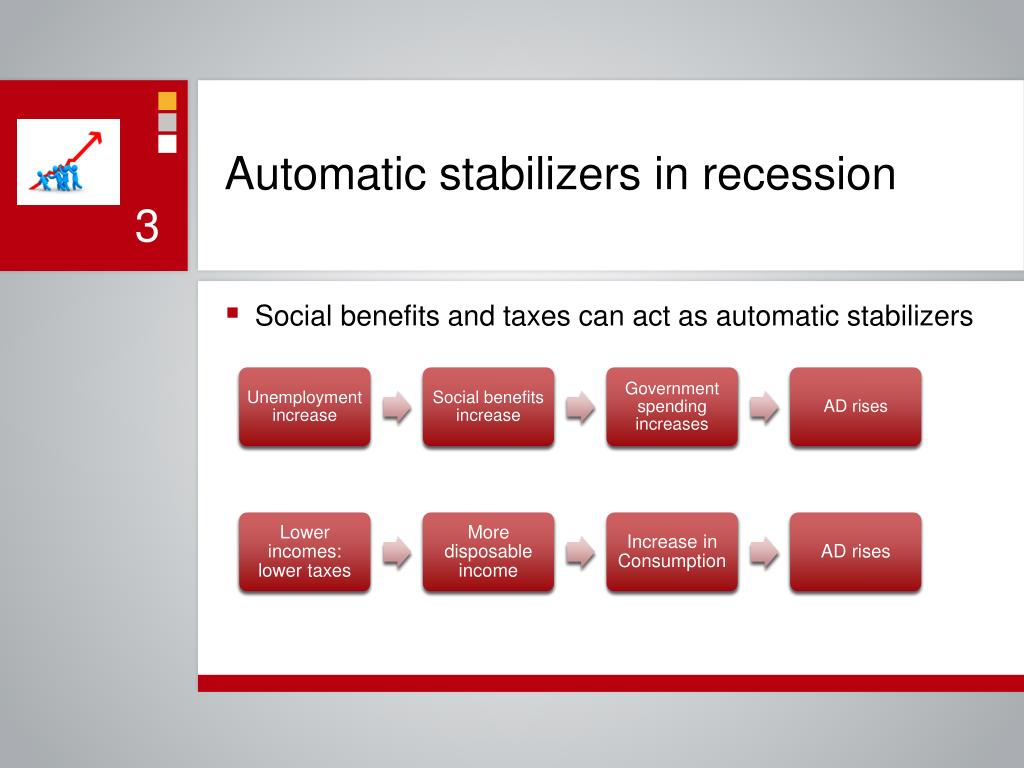
Tax revenues generally depend on household income and the pace of economic activity.

Therefore, automatic stabilizers tend to reduce the size of the fluctuations in a country's GDP. Similarly, the budget deficit tends to decrease during booms, which pulls back on aggregate demand. This effect happens automatically depending on GDP and household income, without any explicit policy action by the government, and acts to reduce the severity of recessions. The size of the government budget deficit tends to increase when a country enters a recession, which tends to keep national income higher by maintaining aggregate demand. That might happen because of belief that in the future taxes might go even higher than before, to compensate for possible losses now.In macroeconomics, automatic stabilizers are features of the structure of modern government budgets, particularly income taxes and welfare spending, that act to damp out fluctuations in real GDP. If taxes are decreased, people might start saving the extra income and the expansionary fiscal policy does not work (or its effect is smaller).This is how government spending “crowds out ” private investment. Private sector, in order to compete with the government, increases its interest rate, thus discouraging private investment. “Crowding out” – governments borrow to increase their expenditure and offer a high interest rate on their bonds.Political influence: where the government expenditure goes and taxes can be used by politicians for electoral purposes.taxes are decreased, workers have more disposable income the very next payday -> consume more right away.) Yet, this point is debatable! Government expenditure is a direct impact on the AD (it changes, various determinants only influence the size of the effect).It can target certain sectors of the economy.Providing incentives for firms to invest: for example, lower corporate tax rate is the obvious incentive.That makes private firms more likely to invest and set up business in the country.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
